

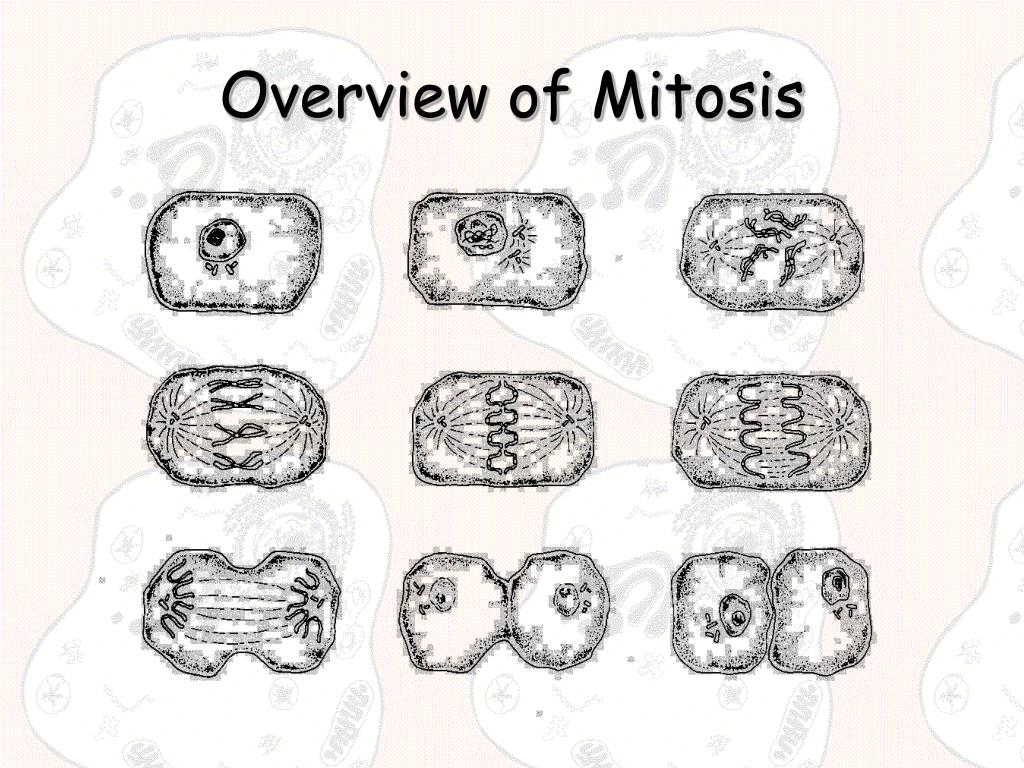
Meiosis, on the other hand, is the process by which cells divide to produce gametes, or sex cells. Finally, in telophase, two new nuclei form and a new cell membrane begins to form around each nucleus. In anaphase, the chromatids are separated and pulled to opposite poles of the cell. During metaphase, the chromatids line up at the center of the cell. In prophase, the chromatids, or strands of DNA, begin to condense and become visible. The process of mitosis can be broken down into four main phases: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During mitosis, the cell's nucleus divides into two, with each daughter cell receiving one copy of the genetic material. This process occurs in all types of cells in the body and is responsible for the growth and repair of tissues. Mitosis is the process by which a single cell divides into two identical daughter cells. While both processes involve the splitting of a cell into two daughter cells, there are some key differences between mitosis and meiosis. Both processes are essential for the continuation of life, as they allow for the production of new cells and the maintenance of genetic diversity.


Many eukaryotes like fungi, sponges, and certain plants are reproduced using budding.
Basically the prokaryotes show binary fission.So the parent or old individual is still there without any change, but in binary fission, the old individual is split into two new individuals. In budding, a new individual is formed on the old individual.It only results in two identical individuals by splitting the parent cell into two parts with mitotic cell division followed by cytokinesis. Major difference between binary fission and budding is that in budding there is an outgrowth from the parent individual producing a bud, which is identical to its parent individual, but in binary fission, there is no bud or outgrowth formation.It is a process in which the parent individual produces a smaller individual known as a ‘bud’ by mitotic cell division. Here, the replication of the nucleus followed by unequal cytokinesis takes place. In the binary fission, two identical individuals are formed.īudding- Budding is also a simple asexual reproduction method seen in fungi, certain plants, and in sponges like Hydra. It involves one parent individual and results in genetically identical individuals, also known as clones.īinary Fission- Binary fission is a simple reproduction method which involves mitosis followed by the splitting of a parent individual. Production of offspring without fertilization is known as asexual reproduction.Īsexual reproduction can be seen in almost all the prokaryotes, some plants, and in certain animals.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
